Carrier sense multiple access (CSMA)
Carrier sense multiple access (CSMA) is a mac protocol in which a transmitting node verifies the absence of traffic on the shared medium/channel before transmitting its data on the medium which is shared by multiple nodes i.e. CSMA is based on the principle "sense before transmit" or "listen before talk”.
Carrier sense means that a transmitting node receives a feedback from the receiver to detect if receiver is busy with other station/node and if the receiver is found to be busy the transmitter waits until the receiver free before transmitting the its own data.
Multiple access means that multiple stations send and receive on the same shared medium. Transmissions by one node are generally received by all other stations connected to through the medium.
CSMA protocol was developed to solve the problem found in ALOHA i.e. to minimize the chances of collision or interference, so as to improve the performance. CSMA protocol is based on the principle of 'carrier sense'. The station senses the carrier or channel before transmitting a frame. It means the station checks the state of channel, whether it is idle or busy.
Even though all the nodes attempt to sense whether the channel is in use, there is still chance that two stations will attempt at the same time to access the medium it is because the stations will only sense at their node and not the whole medium or communication path and because of propagation delay at one node may result in collision of data from other node means The frame transmitted by one station takes some time to reach other stations. In the meantime, other stations may sense the channel to be free and transmit their frames. This results in the collision.
There Are Three Different Type of CSMA Protocols
- 1-persistent CSMA
- Non- Persistent CSMA
- p-persistent CSMA
1) 1-persistent CSMA
- In this before sending the data, the station first listen to the channel to see if anyone else is transmitting the data at the moment.
- If the station sense the channel idle, the station transmits a frame.
- And if the channel is busy, then it sense the transmission medium continuously until it become idle.
- Since the station transmits the frame with the probability of 1 when the carrier or channel is idle, this scheme of CSMA is called as 1-persistent CSMA
Drawback of I-persistent
The propagation delay has an important effect in the performance of the protocol. The more the propagation delay, and the worse the performance of the protocol.
Because of this propagation delay there are still high chances of collision.
(2) Non-persistent CSMA
- In Non-persistent CSMA the station, senses the channel before sending and If no one else is sending, the station begins sending the frames on the channel.
- However, if the channel is already in busy, the station does not continuously sense the channel and will wait for random amount of time before sensing the channel again for the purpose of seizing it immediately upon detecting the end of the previous transmission.
- This algorithm leads to better channel utilization but longer delay than 1-persistent CSMA.
Advantage of non-persistent
- It reduces the chance of collision because the stations wait a random amount of time. It is not like 1-persistent CSMA where two or more stations will wait for same amount of time and will retransmit at the same time.
Disadvantage of non-persistent
- It reduces the efficiency of network because the channel may remain idle until the station again sense the channel after random amount of time.
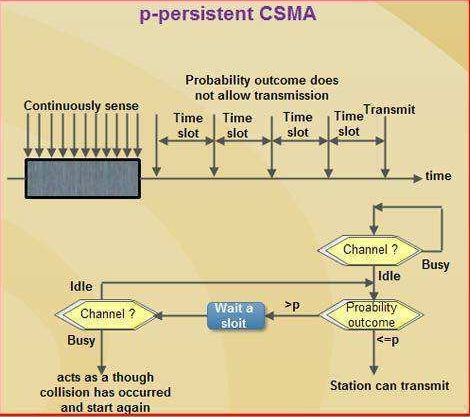
(3) p-persistent CSMA
- This method is used in slotted channels.
- Whenever a station becomes ready to send, it senses the channel.
- If channel is busy, station waits until next slot.
- If channel is idle, it transmits with a probability p.
- With the probability Q=1-P, the station then waits for the beginning of the next time slot.
- If the next slot is also idle, it either transmits or waits again, with probabilities P and Q.
- This process is repeated till either frame has been transmitted or another station has begun transmitting.
- In case of the transmission by another station, the station acts as if there had been a collision (i.e., it waits a random amount of time and starts again).
Advantage of p-persistent
- It reduces the chance of collision and improves the efficiency of the network.



Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not post any spam link in comment box