Layered Architecture
Protocol Hierarchy
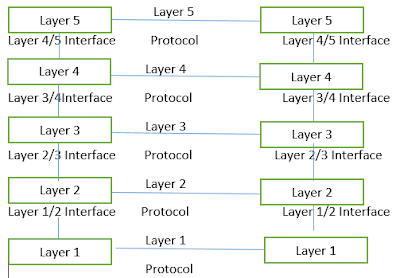
To tackle with the design complexity most of the networks are organize as a set of layers or levels. The fundamental idea of layered architecture is to divide the design into small pieces. The layering provides modularity to the network design. The main duty of each layer is to provide offer services to higher layers, and provide abstraction. The main benefits of layered architecture are modularity and clear interfaces.
Five Layered Network
Design Issues:
Layered architecture in computer network design
Layered architectures have several advantages. Some of them are,
- Modularity and clear interface
- Provide flexibility to modify network services
- Ensure independence of layers
- Management of network architecture is easy
- Each layer can be analysed and tested independent of other layers
Interfaces and Services:
The benefits to layering networking protocol specifications are many including:
- Interoperability - Layering promotes greater interoperability between devices from different manufacturers and even between different generations of the same type of device from the same manufacturer.
- Greater Compatibility - One of the greatest of all the benefits of using a hierarchal or layered approach to networking and communications protocols is the greater compatibility between devices, systems and networks that this delivers.
- Better Flexibility - Layering and the greater compatibility that it delivers goes a long way to improving the flexibility. Particularly in terms of options and choices.
- Increased Life Expectancy - Increased product working life expectancies as backwards compatibility is made considerably easier. Devices from different technology generations can co-exist thus the older units do not get discarded immediately newer technologies are adopted.
- Scalability - Experience has shown that a layered or hierarchal approach to networking protocol design and implementation scales better than the horizontal approach.
- Mobility - Greater mobility is more readily delivered whenever we adopt the layered and segmented strategies into our architectural design
- Cost Effective Quality - The layered approach has proven time again and again to be the most economical way of developing and implementing any system be they are small, simple, large or complex makes no difference. This ease of development and implementation translates to greater efficiency and effectiveness which in turn translates into greater economic rationalization and cheaper products while not compromising quality.
- Standardization and Certification - The layered approach to networking protocol specifications facilitates a more streamlined and simplified standardization and certification process; particularly from an "industry" point of view. This is due to the clearer and more distinct definition and demarcation of what functions occur at each layer when the layered approach is taken.
- Rapid Application Development (RAD) - Workloads can be evenly distributed which means that multiple activities can be conducted in parallel thereby reducing the time taken to develop, debug, optimize and package new technologies ready for production implementation.
Comments
Post a Comment
Please do not post any spam link in comment box